
February 11, 2026
How to Exclude a Country from Google Analytics 4 (6 ways)
Updated: February 11th, 2026
This tutorial will show you multiple ways to exclude a country from Google Analytics 4 reports. Why? Maybe you want to exclude countries where you don’t have any marketing campaigns or business operations to reduce the amount of data being processed.
Whatever your reasons, if excluding countries is what you’re interested in, this is the tutorial for you!
First, I’ll start with the temporary solutions (it means that GA4 still collects that data, but you can exclude it from certain reports). Then, I’ll show more permanent solutions that prevent data (of particular countries) from reaching your GA4 property.
Table of Contents
Here’s what you will learn in this article
- Comparison: Temporary vs. Permanent Exclusion
- Temporarily exclude a country in GA4
- Permanently exclude countries from GA4
- Final Words
Video tutorial
If you prefer video content, here’s a tutorial from my Youtube channel.
Comparison: Temporary vs. Permanent Exclusion
This table gives a quick overview of the two ways to exclude a country in GA4. We’ll go through each option in detail later to help you make the right choice.
| Feature | Temporary Methods (Filters/Segments) |
Permanent Methods (GTM/Server-side) |
| Data Storage | All data is stored in GA4 | Excluded data never reaches GA4 |
| Retroactivity | Can be applied to historical data | Not retroactive |
| Best For | Ad-hoc analysis and comparisons | Reducing data volume/operational focus |
| Technical Level | Beginner (GA4 Interface) | Advanced (GTM/Developer) |
Temporarily exclude a country from Google Analytics 4
Let’s look at a few ways to exclude countries from your GA4 reports temporarily. This is for when you still want to keep all country data but don’t necessarily want to look at users from all countries all the time.

Comparisons in standard reports
Comparisons in Google Analytics allow you to compare different data subsets in standard reports quickly. We will use comparisons to create a subset of data excluding the country (or countries) you don’t want to see!
In Google Analytics 4, go to Reports in the left-side navigation and click any report that you are interested in. At the top of the report, you will see “Add comparisons”. Click this.
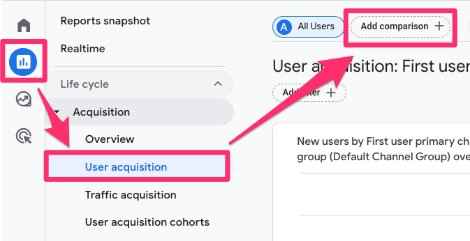
Select “New comparison”.
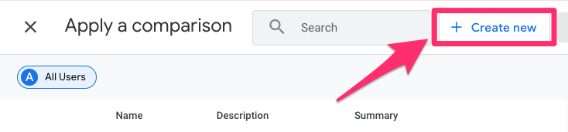
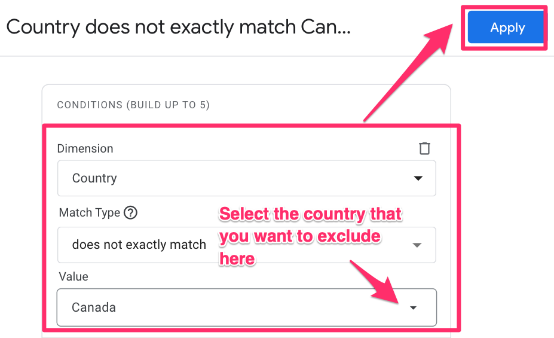
From the dropdown, choose “country” as the dimension, and for the Match Type, select “does not exactly match”. Enter the country(ies) to exclude and click “Apply”. If you want to exclude multiple countries at once, you’ll need to use the Regex (regular expression) option.
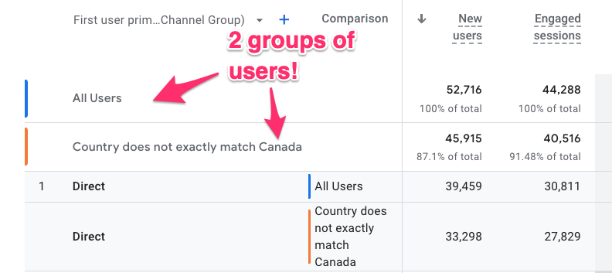
Now, the data has been split into two groups; one has all the data, and the other one has the data without the countries you excluded so that you can compare the two groups.
If you want to remove the “All users” group so you only see data for the comparison you made, you can click the “x” next to the comparison to remove it.
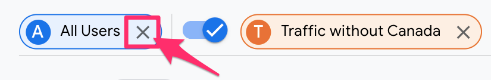
If you go to another report, the comparison will remain, but you must toggle on “View comparisons”.
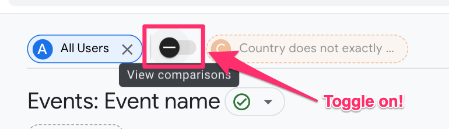
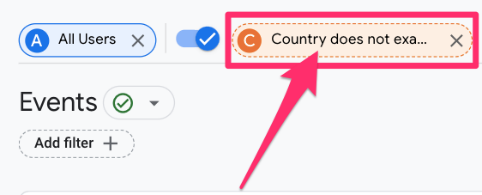
Creating and adding a comparison to a report will only apply to you; other users will not see the change in the reports. To allow others in the property access to the comparison you created, click the comparison you just made at the top of the report.
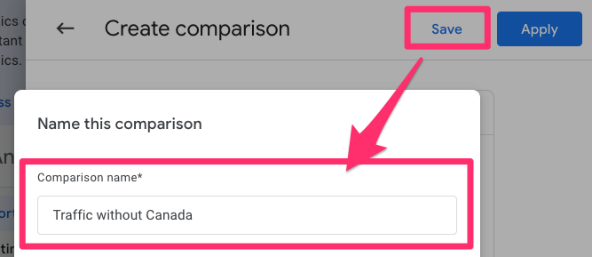
When the popup opens, select “Save”. Name it something like “Traffic without country” (where you replace country with the country or countries you are excluding).
To add an existing comparison, click the “Add comparison” button in the top-right of the report and choose the comparison that you want to apply to the report.
![]()
Filter in standard reports
You can only apply filters to detail reports, which are the reports that have a detailed table at the bottom, like the User acquisition or Events reports.
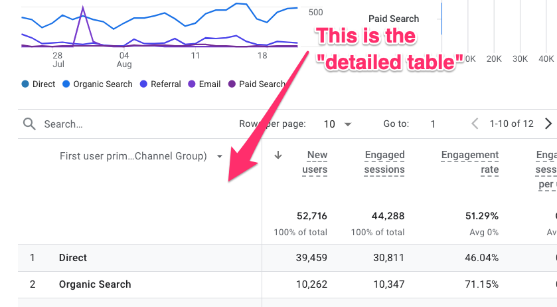
At the top of the report, click “Add filter”.
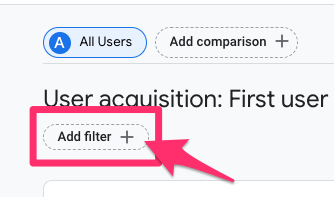
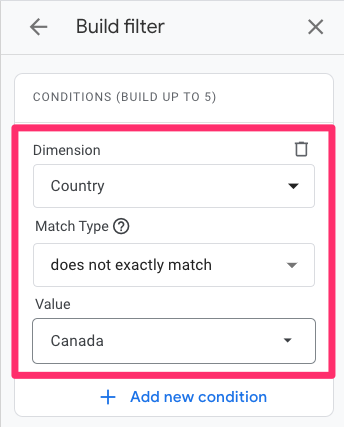
Select “country” as the dimension, and for the Match Type, select “does not exactly match” (if you’re excluding multiple countries, you will need to use “does not match regex”). Enter the country(ies) to exclude and click “Apply”.
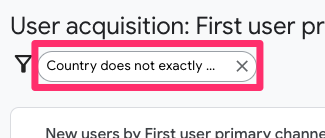
The filter will appear next to the filter icon at the top of the report. This will affect all the data in the report.
One thing you need to understand is that the aforementioned usage of filters is visible only to you (and not other users of the same GA4 property).
If you want to filter a report so that all users would see the same thing, you will need to customize a report. Open a detail report where you want to add a filter. If you have enough permissions, you will see a pencil icon. Click it.
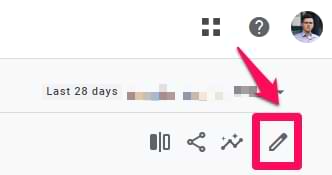
On the right sidebar, click “Add filter” and then exclude the country. After you save the report, this filter will be applied to everyone who opens the report.

Segments in GA4 explorations
You can create a segment that excludes all traffic from a certain country (or countries), and you can have a segment that contains a different subset of data to compare dimensions and metrics.
Or, you can just create the segment and have the entire report only show data that fits the segment. This is useful since it allows you just to save the segment and repeatedly use it in other tabs of your report (the Variables tab stays the same across the tabs of the same report).
In GA4, go to Explore in the left-side navigation and select “Blank report”.
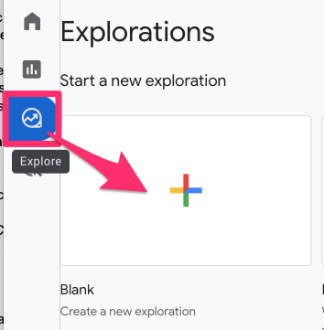
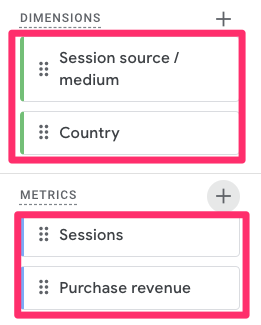
In the report, load in the Dimensions and Metrics below, and double-click to add to the report (other than the Country metric). This is just an example, so you can add whichever dimensions and metrics you want to see.
- Dimensions: Session source / medium & Country
- Metrics: Sessions & Purchase revenue
Click “+” next to Segments in the Variables tab.
Choose “Session segment”. If you want to learn about the differences between the types of segments, read this blog post or check out my GA4 course (for this and much more).

Remove the existing inclusion group and add an exclusion group.
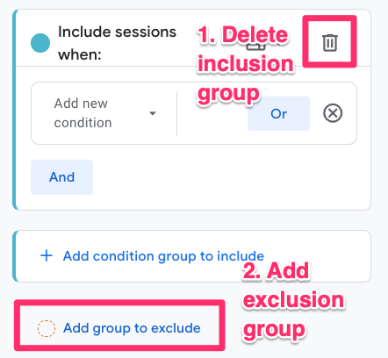
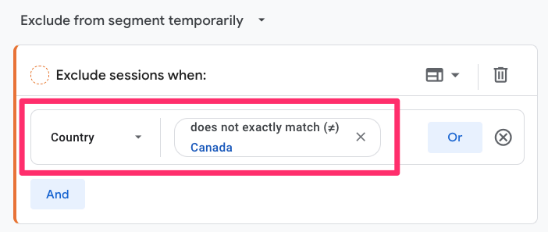
Select “country” as the dimension, and for the Match Type, select “does not exactly match” (if you’re excluding multiple countries, you will need to use “does not match regex”). Enter the country(ies) to exclude, name the segment “Traffic without {country}” and click “Save and apply”.
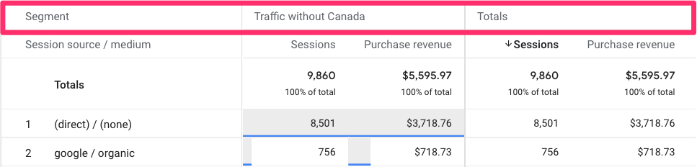
Double-click on the segment you just created to apply it to the report. Now, you will see the data split between the segment you made and the total of all users.
Filters in explorations
You can apply filters to most of the exploration techniques to exclude activity from certain countries (very similar to what we did above).
We will build the same report base as we did for segments, so if you have already done that, you can use the same report. If not, you can follow the instructions below:
- In GA4, go to Explore in the left-side navigation and select “Blank report”.

- In the report, load in the Dimensions and Metrics below, and double-click to add to the report (other than the Country metric). This is just an example, so you can add whichever dimensions and metrics you want to see.
- Dimensions: Source source / medium & Country
- Metrics: Sessions & Purchase revenue

You will see a Filters section at the bottom of the Settings tab. To add a report, you need to:
- Select “country” as the dimension
- Choose “does not exactly match” as the Match Type (you will need to use “does not match regex” if you want to exclude multiple countries)
- Enter the country(ies) you are excluding
- Click “Apply”
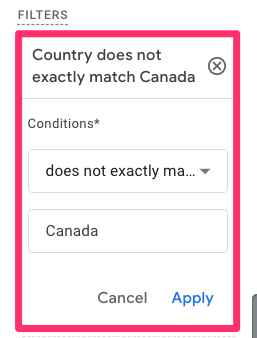
Note: You may notice slight discrepancies in your numbers when comparing segments and filters. This is because segments are typically session-scoped (filtering the entire user journey), whereas standard report filters work like event-scoped segments. This nuance is important for making sure your data analysis remains accurate across different reporting techniques.
Permanently exclude a country from Google Analytics 4
If it’s not enough just to exclude activity for certain countries in your GA4 ad hoc, there are options for how you can permanently exclude a country from GA4.
Keep in mind that this will stop any data from these countries entering GA4, so you will not be able to retrieve the lost information down the line if you change your mind!
With the help of a developer
Suppose you are lucky enough to have a developer on your team (or you yourself are a developer). In that case, you can push country information to the Data Layer before Google Tag Manager loads. From this data, you can create a blocking trigger in Google Tag Manager to ensure GA4 does not fire when a user comes from the excluded countries.
Learn more about the Data Layer by taking my GTM Masterclass
Once the developer has pushed the country in the Data Layer, confirm using Preview Mode. Look for the Message event and check that the country information is available.
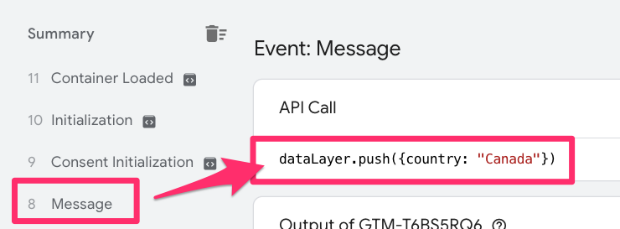
Go to Google Tag Manager > Variables > New User-Defined Variable.
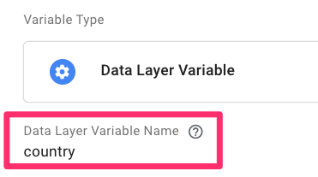
Click “Variable configuration” and choose “Data Layer Variable”.
Enter the name of the Data Layer variable exactly as it is the code (what your developer named it). Name the variable and save it.
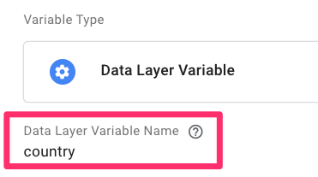
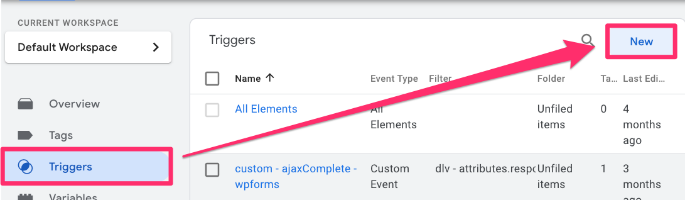
Next, head to Triggers and click “New”.
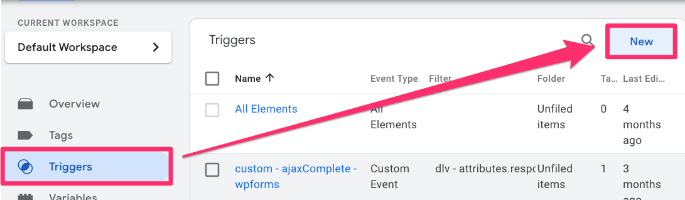
In the Trigger configuration, find “Custom event”.

Input “.*” into the Event name. In RegEx, this means we want the trigger to fire on any event.
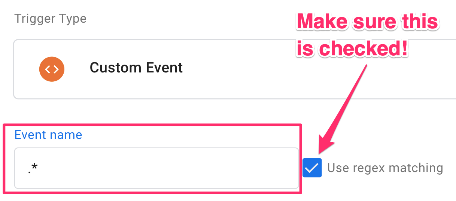
But we only want this trigger to fire when the country code variable captures a certain value. So, select “Some custom events”. Set the filter to dlv – country equals “{the country code you want to exclude}”. Name the trigger “blocking – country traffic”.
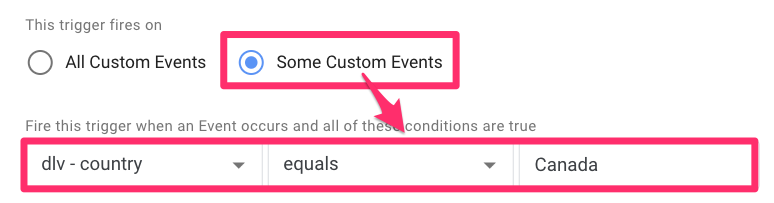
Note: Using “equals” may seem weird since we were using “doesnot exactly match” in the GA4 interface. But, here, we want the trigger to block certain users from being tracked, so we need it to fire when the country a user is coming from equals the name of the country we want to exclude.
Go to the GA4 configuration tag (a.k.a. Google Tag), select “Triggering”, then “Add exception”.
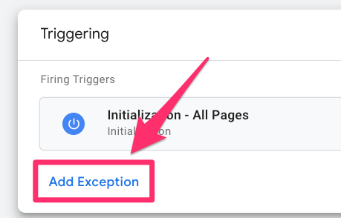
Choose the blocking trigger you just made. Save.
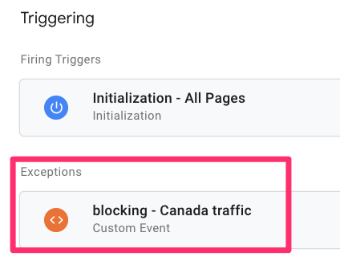
Do the same for all GA4 event tags, too. Alternatively, you can go to Tags and select all tags that you want to block in a particular country.
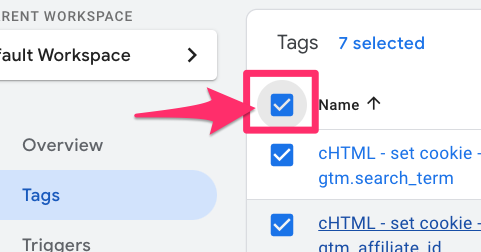
Then, click “Edit Triggers”.
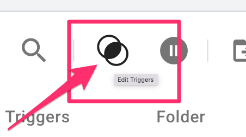
At the very bottom, click “Add exception” and select the blocking trigger you just made. Save these changes.

Once you are confident that the blocking trigger has been applied (either in the config or to each tag), publish the container. Be sure to give it a name and description if you need to refer back to the changes you made!
Without the help of a developer (but with server-side tagging)
This last option in this blog post requires you to use server-side tagging. It offers a more robust way to exclude countries because the exclusion logic happens on your own server rather than in the user’s browser.
This makes the exclusion more reliable and helps you maintain a clean data stream even when browser-side scripts are interrupted. This tutorial will not cover what server-side tagging is, so check out the server-side tagging article if you want to learn more.

Use Preview mode to launch your site and check the Event Data for any events that come through. You want to look for anything related to “country” (you may not be collecting this value, so this will only work if you are).
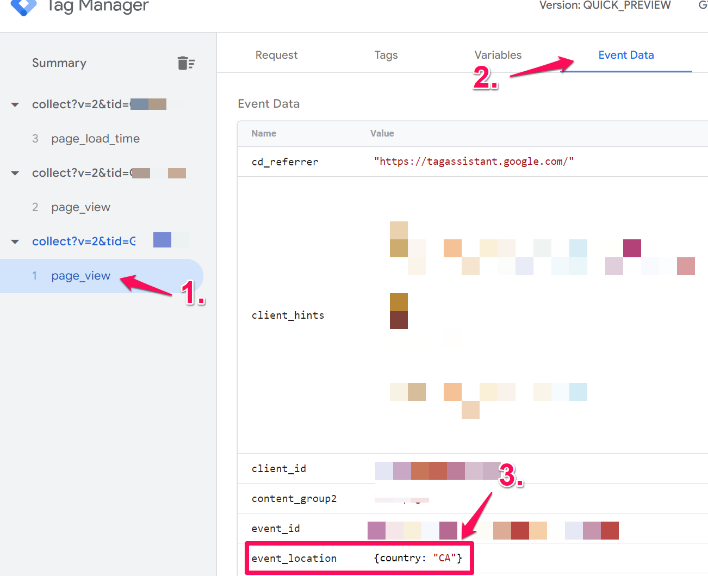
Assuming you have found this information somewhere, you will follow a similar path as the previous example but adjust it to be relevant for your server-side container.
In my case, the country data is found in the event_location.
Go to Variables and under User-Defined Variable click “New”.
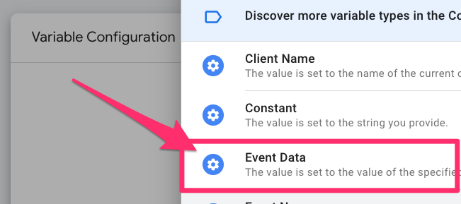
For the variable configuration, choose “Event Data”.
Enter the key path of the variable (the same as the name you see in Preview mode). Name this “event data – event_location.country”. This may be different for you, so name how it shows up in your data.
I used event_location.country because, in the preview mode, I saw the event_location object, which contains a country key.
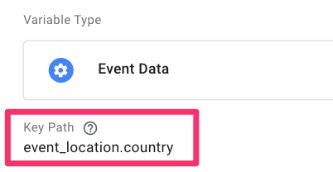
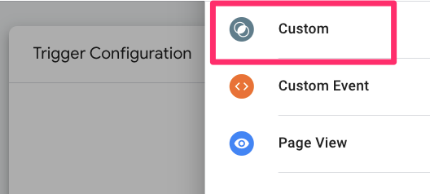
Go to Triggers and click “New”. For the trigger configuration, select “Custom”.
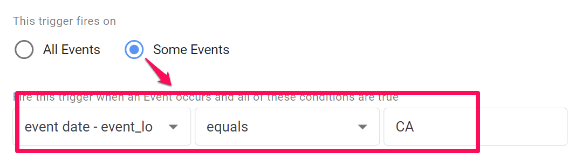
Toggle “Some Events” and find event data – event_location.country in the dropdown and set it equal to the country you are excluding. Name the trigger “blocking – {country}”.
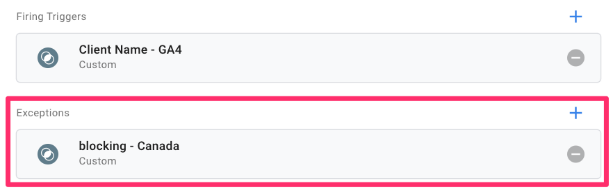
Go to the GA4 tag and under “Triggering” click “Add Exception”. Select the blocking trigger from above.
If you want to test if this is working properly, you might need to use a VPN service (NordVPN, Surfshark, etc.) that allows you to browse from that excluded country. Once you have connected, enable the server-side GTM preview mode and check if your GA4 tags are not fired.
Frequently asked questions
Is excluding a country in GA4 retroactive? No. Permanent exclusion methods, such as GTM blocking triggers or GA4 data filters, only apply to data collected after the filter is set to “Active”.
How can I test if a country exclusion is working? Use a VPN service to browse your site from the excluded country while viewing the GTM or GA4 DebugView to make sure your tags are not firing.
Exclude a Country from Google Analytics 4: Final Words
Whether you want to temporarily exclude data from a specific country or permanently exclude data from a particular country, there is a solution for you!
Remember, excluding country traffic using GA4 data filters is not retroactive; it will only apply to data collected after the filter is set to ‘Active’ and has had time to process. Always test your filter thoroughly in ‘Testing’ mode before activating it to avoid unintended data loss.


1 COMMENT
In the future, it would be very beneficial if you can explain reasons why filtered numbers and segmented numbers are different in GA4 explorations reports.